Information System for Managing the Ionizing Radiations Based Medical Procedures and the Patient Dose
Autor: A. Badoiu, A. Botu, V. Vlad, S. Petrescu, Gh. Matei
The RXINFO project is aimed to implement a web based integrated information system which takes into account the complexity of aspects regarding ionizing radiation medical procedures, with special focus on the radiation dose received by a patient at an exposure and on the management of the image results of the procedures. The information system ensures the possibility that an image registration - result of an ionizing radiation procedure undergone by a patient - to be accessed over Internet by other physicians. Additionally, the system stores the values of the ionizing radiation doses lifelong received by each patient in view to make this data available to any radiology physician within the country.
The access to the information system data is regulated by the in-force legislation regarding the personal data protection, the physicians' author rights and the patients' rights.
I. INTRODUCTION
The project scope is the implementation of an information system aimed to store data associated with ionizing radiation based medical procedures applied to patients all over the country. The system will store in a centralized database the values of the radiation doses received by each patient as well as the web addresses where the corresponding resulted images are available. The access to the stored data will be granted to the radiology physicians, based on identity/ authentication information.
The system will also implement the electronic signature function as the main element of authentication for the radiology physician. The images resulting of procedures will be stored into the local databases of the medical units where they were performed. These databases will be interconnected ensuring a secured access for the radiology physicians.
The data transferred over the Internet will be encrypted, using the PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) mechanism, based on the pair of keys public key - private key.
The system will provide the radiology physician information regarding the ionizing radiation doses received previously by the respective patient, helping him to take a decision related to the opportunity of a new exposure to radiation. Also, the radiology physician will be able to access, via the information system, the databases where images resulted from former undergone investigations are stored.
The main beneficiary of the project results is the patient himself. Other beneficiary is the medical personnel of the health centers where ionizing radiation based investigations are performed, who can establish patients' diagnosis more accurately. The exploit of RXINFO information system avoids unnecessary repeated investigations determining important savings in the health system costs. The information system will be given in administration to CNCAN (National Committee for the Nuclear Activities Control) while system components will be implemented at radiology centers across the country.
According to the National and European regulations in the field, it is necessary that the medical radiology equipment used to perform high risk of irradiation investigations (radioscopy, angiography, coronarography, radiology, interventional radiology, pediatrics), as well as the mobile radiology devices, to be equipped with systems able to measure the Dose-Area Parameter (DAP) and/or patient received dose.
Presently, the dose value received by a patient is hold locally on a paper register. Compliant with the law, these data must be reported periodically for enabling, at regional and national level, the evaluation of the population exposure at radiations and consequently the actions to be taken for reducing it. These evaluations based on collecting data registered on paper from individual clinics have a statistic character and can't prevent the accumulation of significant dose of radiation at patients' level.
Also, the images resulted during medical investigations are actually stored in the clinic database while a copy on physical support is handed to the patient. If a physician wants to see previous images resulted from investigations performed in other clinic to a patient, or to find out the radiation dose received by the patient during previous examinations, he had to contact personally the physician which have performed the investigation.
Practically, this doesn't happen and in consequence the patient is submitted to new ionizing radiation procedures, without being known the formerly received radiation doses or the image results of the tests.
II. DESCRIPTION OF THE INFORMATION SYSTEM
The RXINFO system have two major components, namely a central subsystem which will host the national database and local subsystems placed at the clinics which perform ionizing radiation based procedures, as can be seen in Fig.1.
The system main stockholders are:
- the providers of health services based on ionizing radiations;
- the radiation hygiene regional laboratories;
- the patients;
- the persons in charge of the Ministry of Health and public health authorities;
- the Internet users.
For each user category there are defined separate access rights, each category being permitted to access only specific category of information.
The main central subsystem functions can be divided into three groups:
- collection and storage of data received from the local subsystems installed at the premises of the health services based on ionizing radiations providers; this function has two components: one refers at the collection and storage of data resulting from procedures into the system database and the other at the collection and storage of the image results into the system structure of files;
- specific information delivery targeted to authorized users, as reports generated by the information system;
- public information delivery targeted to all users.
The central subsystem functions determine its structure as presented in Figure 2.
At the central level, the following main data will be registered into the database for each patient and each procedure:
- the date and the time of procedure;
- the medical unit where the procedure is performed;
- the number of radiation exposures during the procedure;
- the ionizing radiation dose received at one exposure;
- data regarding the radiology physician which performs the procedure;
- the procedure image results or the web address where the procedure image results can be found.
The local subsystem (Fig. 3) is basically a RDBMS (Relational Data Base Management System) accessible over the Internet.
The local subsystem functions are as following:
- collection and local storage of the data resulted from the medical procedures based on ionizing radiations performed by the provider;
- local reports generation;
- communication with the central subsystem over Internet, for transmission of the investigations results.
The information stored into the central subsystem database will be continuously updated by the local subsystems, by means of web services.
During a radiation based procedure performed to a patient, the data introduced by the physician into the local database will be automatically transmitted and stored into the central database. Additionally to data regarding the patients� radiation doses, the local databases will store the procedures image results. As it was previously mentioned, into the central database will be also stored data pointing where the procedure image results can be found (metadata).
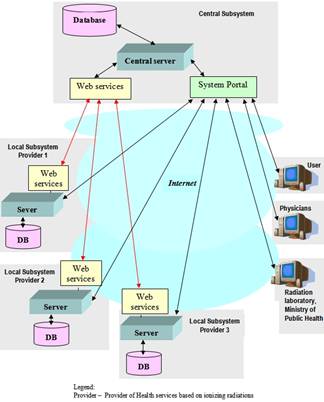
Figure 1. System general architecture
Any radiology physician may access the information system in the following situations:
- to get informations about the previous X-rays doses received by a patient;
- to get information about the image results of the procedures that the patient has undergone in other health units;
- to download / visualize the image results of the previous procedures that the patient has undergone in other health units.
The local subsytems consists of local database and a web software application that performs the management of the local database and of the securized access for radiology specialists. The local subsystem will be available both to the clinic personnel via the local Intranet and to other physicians across the country who will access it over Internet.
The image results of medical procedures will be registred and stored into the databases in a format which ensures the interoperability with other operating systems and equipment.
Another signficant issue is the security of the patient data. Consequently, before transmission the data will be encrypted and then decrypted at the destination. The encryption will be performed by means of PKI (Public Key Infrastructure). For any local subsystem an unique pair of keys (one public and one private) will be generated.
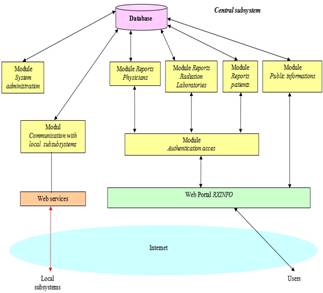
Figure 2. Central subsystem architecture
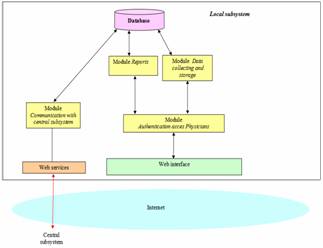
Figure 3. Local subsystem architecture
The public keys will be stored at the central information subsystem, together with the owners' identification data (radiology physicians).
The key ring will enable each physician to create his own digital signature.
Before being transmitted from a local subsystem to other, the resulting image files will be encrypted. The access via Internet of any physician to the patient�s data will be achieved only with the patient's written permission, in compliance with the law.
The Internet data transfer will take place using web services which enable the data exchange between various applications, consequently between databases, no matter the technology they were implemented.
Several main technical characteristics of the system are enumerated bellow:
- by concept the system will have a modular and flexible structure aimed to cover all the required functions;
- the system will be scalable; its performances will not depend on the database size or on the number of data transfers between the subsystems;
- the system will be wide configurable regarding various types of medical procedure/ equipment/ data file format etc;
- the system will implement SOA architecture in order to ensure a high degree of interoperability.
III. TECHNOLOGIES
The system is being developed using the web technologies.
Thus, at data level the database management is performed using Oracle Database 10g Server while the application level (business logic) is developed using open-source software technologies as PHP and JavaScript.
The communication software implements web services using open standard technologies as XML and SOAP.
The data encryption procedure will implement the PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) mechanism and programs as PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) will be employed.
The system presentation level (user interface) will consists of a national web portal integrated within the central subsystem.
IV. SIGNIFICANT ELEMENTS AND ETHICAL ISSUES
An important issue of implementing RXINFO system is the national scale storage of the information collected as result of the ionizing radiations based procedures and the opportunity offered to each radiology physician to access the information system from anywhere.
The system comprises, besides its central component, the local databases belonging to different radiology units placed all over the country, aiming to make available the local stored data. The innovative element in this case is the heterogeneous database interoperability provided within the system as well as interoperability between the various formats of the multimedia files stored into the databases.
The inclusion of CAD (Computer Aided Diagnosis) methods and technologies associated with the image results of the medical investigations represents an other major issue. The information system is designed to have a distributed structure, based on data communications.
Regarding the data exchange over web, the system uses innovative web services to ensure interoperability with the existing heterogeneous databases. The communication within the information system employs encrypted data as well as the electronic signature as an important security issue.
The complexity of the system is determined by the great amount of information to be structured and stored into the distributed databases.
The main ethical aspects implied within the project are related to the confidentiality of patient data. As mentioned, the information system will employ law compliant methods and procedures (electronic signature and data encryption) for secure access to private personal data.
In the framework of the project, will be carried on studies and analyses on topics as ionizing radiation influences over beings, categories of dedicated equipments in exploit, the usefulness of the digital images in the management of patients submitted to radiologic investigations / therapy, the spread of CAD methods in physicians current activity.
The results of these studies will contribute to structure the information system databases content (the e-content).
The studies conducted within the project does not imply supplementary risks for patients compared with the usual medical investigations.
Another category of ethical aspects is linked with the right of public use of an information, or part of it, protected by author rights.
Usually, this aspect is solved by distinctly emphasizing the information taken over and mentioning its source, if the information was already published in a determined mode, or by obtaining the author's accept for using his creation in any form.
V. PROJECT IMPACT
The RXINFO project develops this field of knowledge by a new approach (sustained by the European and more recently by national legislation), which enables access to secure and confidential data, anytime from anywhere, in compliance with the law.
The large opportunities given by the new investigation methods must be intelligently and rapidly exploited by their inclusion into Internet accessible information systems.
Also, the analysis based on significant case studies of the influence over the general health condition of the radiation dose received by a person represents a contribution to the field knowledge.
By introducing the digital radiology, more efficient workflows are expected, as well as the decrease of search time for patient radiology files.
The physician will have at his disposal more ways to visualize and to process the images, with a complete set of tools.
VI. CONCLUSIONS
The project answers to important issues of the public health system, in accordance with national and European legislation. The project will implement HL7 standard in the domain of healthcare information systems. The resulting information system must be viewed as a pilot, which will continue to be extended after the project is over by inclusion of other ionizing radiations medical centers.
The pilot system feature contributes at project sustainability and the system databases will be available to other organizations with active role in healthcare (Ministry of Public Health, CNCAN - National Committee for the Nuclear Activities Control etc.)
Noutăţi
The RXINFO project is aimed to implement a web based integrated information system which takes into .... Detalii
Sistemul RXINFO
A fost realizat si testat sistemul informatic RXINFO. Sistemul se adreseaza furnizorilor de servicii medicale bazate .... Detalii




